Cryptocurrencies have shaken up the global financial world by providing alternatives to traditional money and banking systems. But not every country is on board with this shift. One of the strongest opponents is China, which has completely banned activities like crypto trading, mining and running exchanges. This strict approach has left many wondering why China is taking such a tough stance, what it means for the global crypto market and how digital assets are treated under the law in the world’s second-largest economy.
This article goes into further detail on China’s total ban on cryptocurrencies, how its rules have changed over time, what the law truly covers and what all of this implies for the future of innovation and the global financial system.
The Timeline: How China’s Crypto Ban Evolved
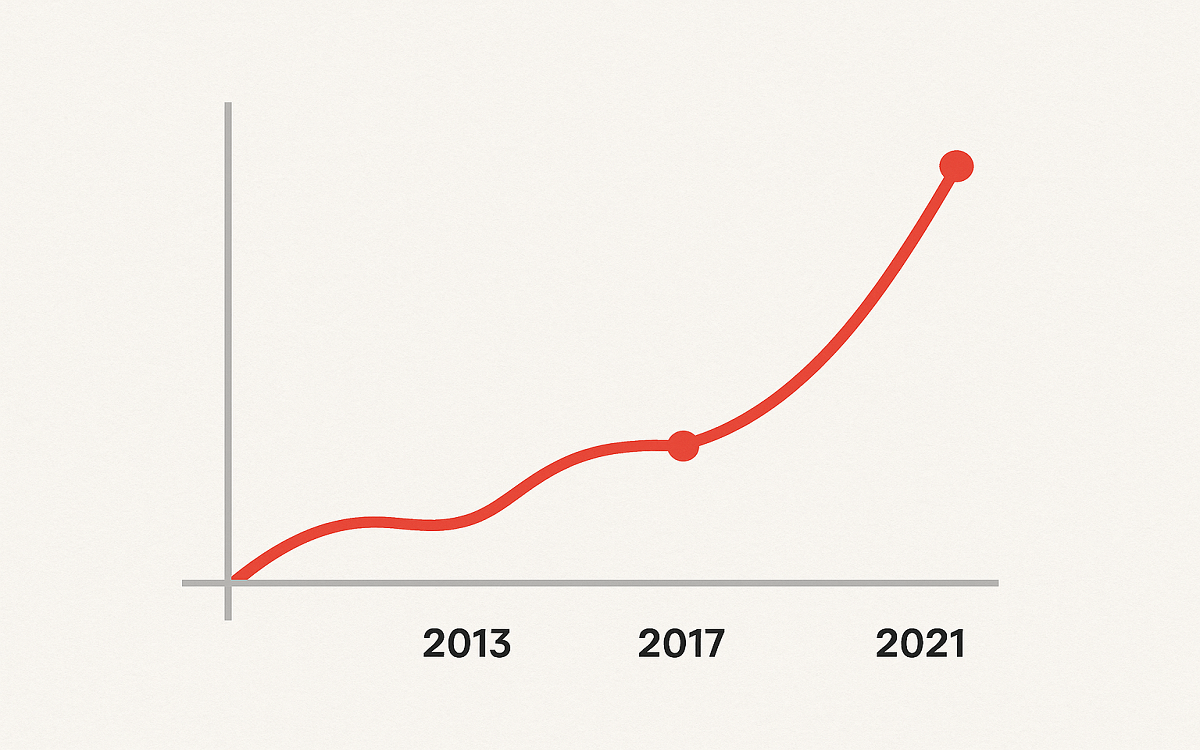
It took some time for China to become wary about cryptocurrency. Since 2013, the rules have been gradually increased, and in 2021, they will be completely prohibited. Here is a quick chronology of significant turning points:
2013 – First Warning
The People’s Bank of China (PBoC) issued its first official warning about Bitcoin by saying it was a virtual commodity instead of real money. Cryptocurrency trading was against the law for banks and other financial organizations.
2017 – ICO Ban and Exchange Closures
Chinese authorities deemed Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) unlawful as they became more well-known, forcing cryptocurrency exchanges such as BTCC and Huobi to cease operations or relocate outside. This dealt a serious hit to Asia’s cryptocurrency market.
2021 – Full Crackdown
In May 2021, the Chinese government launched a nationwide crackdown on crypto mining, pointing to environmental issues and financial risks. A few months later, in September the People’s Bank of China announced that all cryptocurrency transactions were illegal even those from overseas exchanges serving people in China. With that, the country effectively shut down all crypto-related activities.
What’s Banned: A Breakdown of Prohibited Activities?
The 2021 policy update left little room for ambiguity. China made it clear that all cryptocurrency activities fall under the category of “illegal financial activities.” These include:
- Crypto exchanges (domestic and overseas)
- Trading cryptocurrencies (peer-to-peer or through platforms)
- Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs)
- Crypto mining operations
- Crypto payment services
- Token fundraising and derivatives
- Advertising and marketing of crypto services
Furthermore, even if they operate from outside of China, staff members of international cryptocurrency businesses who cater to Chinese citizens may be subject to legal repercussions.
Legal Gray Area: Is Holding Crypto Illegal?
Interestingly, while trading and other crypto-related services are banned, holding cryptocurrencies is not explicitly illegal for individuals. Several Chinese courts have ruled in recent years that cryptocurrencies can be treated as “virtual property” and individuals can hold them as such.
Judicial Precedents:
- The Shanghai High Court declared in May 2022 that Bitcoin is protected by Chinese law as virtual property and is thus protected by property rights.
- However, using crypto for business purposes is still illegal.
So, while citizens may theoretically own crypto, using it in any capacity for payment, investment or exchange is not permitted under the current laws.
Why Did China Ban Crypto?
China’s decision to completely ban cryptocurrencies stems from a mix of economic, political and environmental concerns.
1. Financial Stability
The Chinese government is concerned that unchecked cryptocurrency activity would cause financial system disruptions in the nation. Because of their volatility, susceptibility to speculation and lack of central – bank regulation, cryptocurrencies pose a threat to the state’s monetary authority.
2. Capital Flight
Cryptocurrencies enable cross-border transactions that bypass traditional capital controls. Beijing has strict regulations on capital outflows and crypto offered a loophole, threatening to destabilize the yuan and China’s foreign reserves.
3. Money Laundering and Fraud
Authorities have cited the increased use of crypto in illegal activities, including fraud, pyramid schemes and money laundering. Crypto transactions are hard to track since they are anonymous and decentralized.
4. Environmental Concerns
Before the ban, China accounted for more than 65% of global Bitcoin mining, much of it powered by coal. In a bid to meet carbon neutrality goals, China targeted the energy-intensive crypto mining sector shutting down thousands of operations.
5. Promotion of Digital Yuan (e-CNY)
China is a pioneer in developing Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs). The Digital Yuan (e-CNY) is controlled by the state and offers all the benefits of digital payments without the risks associated with decentralized assets. Banning cryptocurrencies clears the field for the digital yuan to thrive.
Global Impact of China’s Crypto Ban
China’s ban sent shockwaves through the global crypto market:
🪙 Market Volatility
Following the announcements, Bitcoin and other major coins saw dramatic price drops. The uncertainty stemming from the world’s most populous country turning hostile toward crypto triggered panic selling.
⛏️ Mining Exodus
Many operators were compelled to migrate to North America, Central Asia and Eastern Europe as a result of the mining embargo. The United States, Kazakhstan and Russia quickly became the new mining hubs.
🌍 Geopolitical Shift
China’s retreat from crypto has allowed other nations to step in. El Salvador adopted Bitcoin as legal tender, while Dubai, Singapore and Switzerland continued to innovate and attract blockchain investment.
Workarounds: Is Crypto Still Active in China?
There is still some illegal crypto activity going on, even though the government is cracking down on it. Peer-to-peer trading via VPNs and offshore platforms is still going on but it’s becoming riskier.
Some common strategies users employ:
- Over-the-counter (OTC) platforms
- Foreign crypto exchanges accessed via VPNs
- Shell companies or intermediaries for token purchases
Chinese officials, however, are working harder to find and close these subterranean conduits. Those who are detected may be subject to harsh penalties, such as having their property taken or maybe going to jail.
China’s Share in Global Cryptocurrency Adoption
Before the statewide prohibition, a lot of Chinese people and businesses were involved in the worldwide bitcoin industry. China made up around 15% to 20% of all crypto transactions at its height and before the mining restriction, it made up more than 65% of the worldwide Bitcoin hash rate.
Chinese retail investors were also quite active on sites like Binance, Huobiand OKEx, some of which startedin China. China’s huge engagement made it a major player in the early development of crypto markets. This means that the 2021 ban not only hurt consumers in China, but it also changed the way mining and liquidity worked throughout the world.
Impact of China’s Crypto Ban on the Global Market
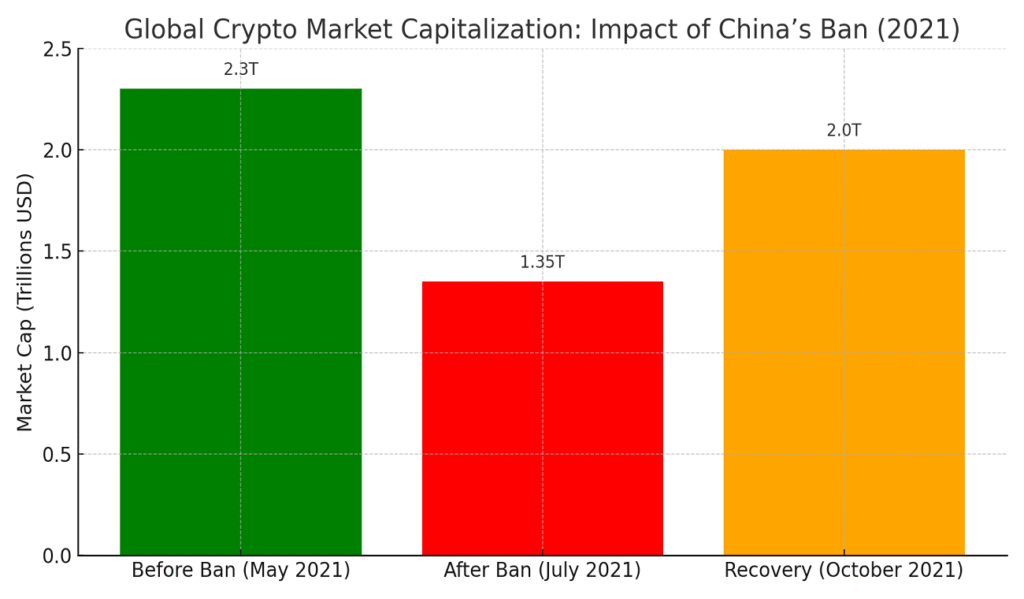
The global cryptocurrency industry was rocked almost instantly in 2021 as China intensified its crackdown on cryptocurrencies. Market capitalization fell precipitously as a result of the restriction, which specifically targeted cryptocurrency trade and mining. The global cryptocurrency market peaked at $2.3 trillion before the crackdown started in May 2021.
Panic selling and investor apprehension as Chinese-based businesses started closing or moving abroad were the main causes of this steep drop. Despite the market’s partial recovery later in the year, the episode demonstrated China’s close ties to the global cryptocurrency ecosystem.
What about Hong Kong?
When it comes to Hong Kong, they play by their own rulebook, not Mainland China’s. Since mid‑2023, the city has given the green light to licensed crypto exchanges and is rolling out the red carpet for Web3 and blockchain startups. It’s quickly gaining a reputation as a crypto hotspot—even if Beijing’s shadow still looms.
- Separate rules from mainland China
- Licensed crypto exchanges welcome
- Strong push for Web3 and blockchain projects
- Fast‑growing crypto hub in Asia
- Still feels Beijing’s influence
Hong Kong demonstrates how to successfully combine innovation and regulation. Maintaining such independence to encourage businesses to stay is now the true problem.
The Road Ahead: Will the Ban Be Lifted?
As of 2025, China hasn’t softened its approach in fact, regulators are doubling down and cracking down harder on crypto and rolling out their own state‑backed digital finance schemes. They’re building a wall around China’s financial system, making it crystal clear that unofficial digital currencies won’t be tolerated.
But tech rarely waits for rules to catch up. Creative minds are quietly experimenting with DeFi platforms, privacy‑focused wallets and clever workarounds to keep crypto alive if only beneath the radar. Small pockets of enthusiasts still trade peer‑to‑peer, share tips in encrypted chats and build underground networks, all hoping to ride the next wave of blockchain innovation despite the odds.
Final Thoughts
China’s all-out ban on cryptocurrencies is a watershed moment in the world of digital money. While places like the U.S. and EU are still hashing out rules, China decided to draw a firm line no crypto at all. They’ve done this deliberately to keep a tight grip on their financial system, push the digital yuan and maintain social stability.
Anyone who wants to use crypto to come up with new ideas can’t go to China right now. But things in money and technology change quickly and nothing lasts forever. China’s decision to stick to its guns or change its mind later will have a big effect on the world of digital currencies.
No matter what happens next, China’s decision will have ramifications on boardrooms and blockchain networks all across the globe.